THROAT
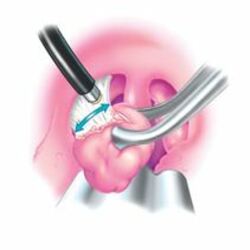
Tonsillectomy
Tonsillectomy is a surgical procedure in which both palatine tonsils are fully removed from the back of the throat.
The procedure is mainly performed for recurrent throat infections and obstructive sleep apnea (OSA). For those with frequent throat infections, surgery results in fewer sore throats in the following one to two years, but unclear long term benefits. In children with OSA it results in improved quality of life.
UPPP
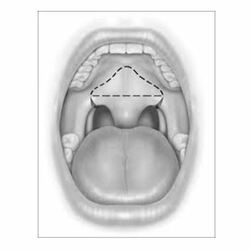
Uvulopalatopharyngoplasty (UPPP) is a surgical procedure to eliminate extra tissues. This procedure increases the oropharyngeal airspace by resecting tissue in the throat, including one or more of the following:
- The uvula the soft flap that hangs down at the back of the throat.
- Parts of the soft palate and tissue at the side of the throat.
- Tonsils and adenoids in the even they are present.
It is currently the may be considered as the most common surgery performed for adults with obstructive sleep apnea. Sleep apnea is one of the causes which left untreated can lead to cardiac conditions.
Snoring evaluation & Surgery for snoring
Snoring evaluation
The diagnosis of snoring is the evaluation based on history and physical examination. Certain cases a specialized sleep study may be required to diagnose snoring. The preferred methods of treatment include, Positioning therapy and weight loss.
Mandibular protrusion splints can reduce snoring in some suitable cases. If breathing through the nose is impaired, Rhinological or Rhinosurgical treatment is advised. For anatomical abnormalities of the soft palate, a suitable minimally invasive surgical procedure can be considered.
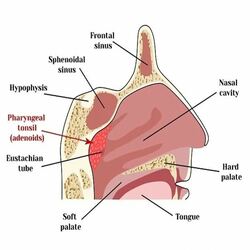
Surgeries for snoring include:
Laser-assisted uvulapalatoplasty (LAUP): LAUP reduces tissue in the soft palate and improves airflow. Radiofrequency ablation:
Somnoplasty: A minimally invasive procedure, also known as Radiofrequency ablation, to reduce the soft tissue in the upper airway or back of the throat. It uses radiofrequency energy to shrink excess tissue in the soft palate and tongue
Tonsillectomy and adenoidectomy: These procedures are used to remove the tonsils and/or adenoids may be needed to prevent snoring.
Vocal nodule
Vocal nodules, also known as singer’s nodules or vocal cord nodules, are benign growths or calluses that form on the vocal cords. They are typically caused by excessive strain or overuse of the vocal cords, and are most commonly found in individuals who use their voice professionally, such as singers, actors, and public speakers. Symptoms of vocal nodules may include hoarseness, difficulty speaking or singing, a scratchy or rough voice, and vocal fatigue. Treatment options may include vocal rest, speech therapy, and in some cases, surgery.
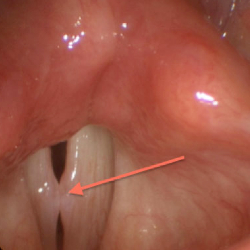
Vocal polyp
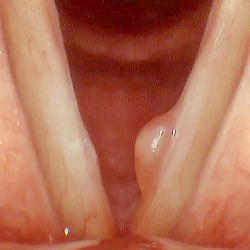
Vocal polyps are non-cancerous growths that develop on the vocal cords. They typically occur as a result of vocal abuse or injury, such as chronic throat clearing, yelling, or singing improperly. Symptoms of vocal polyps may include hoarseness, a breathy or weak voice, a lump or swelling in the throat, and difficulty speaking or singing. Treatment options for vocal polyps may include voice therapy, vocal rest, and in some cases, surgery to remove the polyp. It is important to address vocal polyps promptly, as they can worsen over time and potentially lead to permanent vocal damage if left untreated.
Voice assessment
Voice assessment in ENT involves the evaluation of a patient’s vocal function to diagnose and treat various voice disorders. The assessment typically begins with a comprehensive medical history and physical examination of the patient’s larynx and vocal cords. Additional tests may include acoustic analysis of the voice, which measures factors such as pitch, loudness, and vocal quality, as well as perceptual analysis, which evaluates the listener’s subjective impression of the voice. Other specialized tests such as laryngoscopy or stroboscopy may also be used to visualize the vocal cords during speech or singing. Based on the results of the assessment, the ENT specialist can develop an individualized treatment plan, which may include voice therapy, medication, or surgical intervention.
Swallowing
Swallowing is refers to the process of moving food or liquid from the mouth through the throat and into the esophagus. Swallowing disorders, also known as dysphagia, can occur due to a variety of factors, including neurological conditions, structural abnormalities, or damage to the muscles or nerves involved in swallowing. Symptoms of dysphagia may include coughing or choking during meals, difficulty swallowing, regurgitation of food, and weight loss due to decreased appetite. Evaluation of swallowing in ENT typically involves a detailed medical history and physical examination, as well as imaging studies such as a videofluoroscopic swallowing study or fiberoptic endoscopic evaluation of swallowing. Treatment for swallowing disorders may involve changes to the patient’s diet, swallowing therapy, or surgical intervention to correct structural abnormalities or nerve damage.